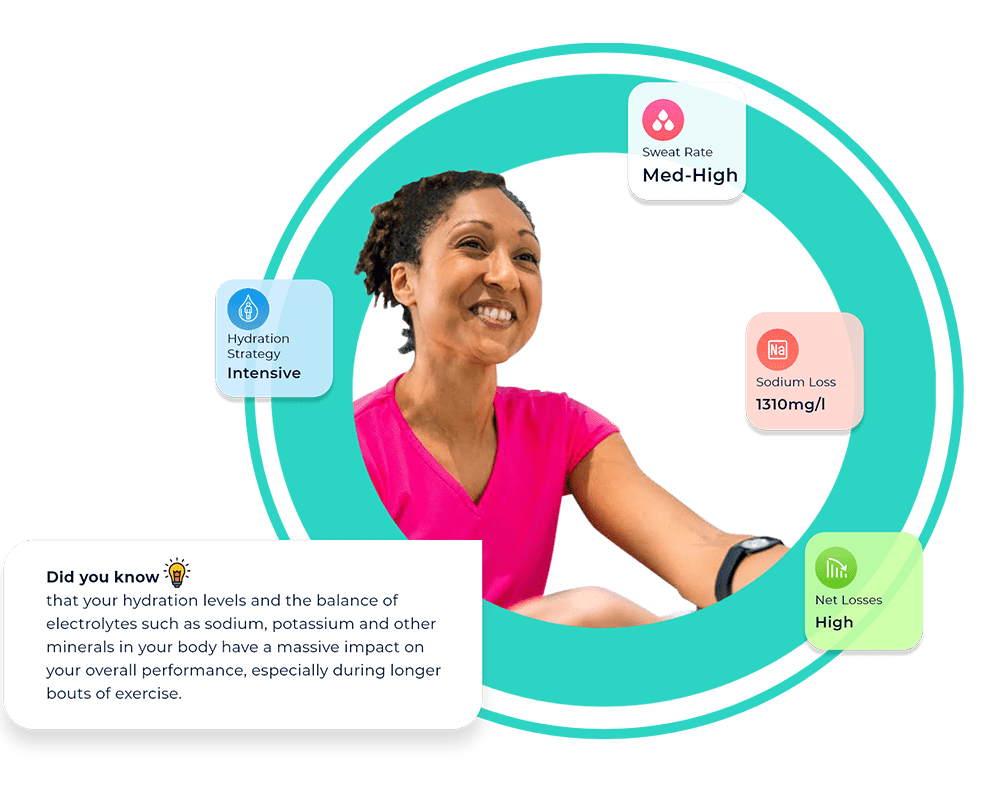
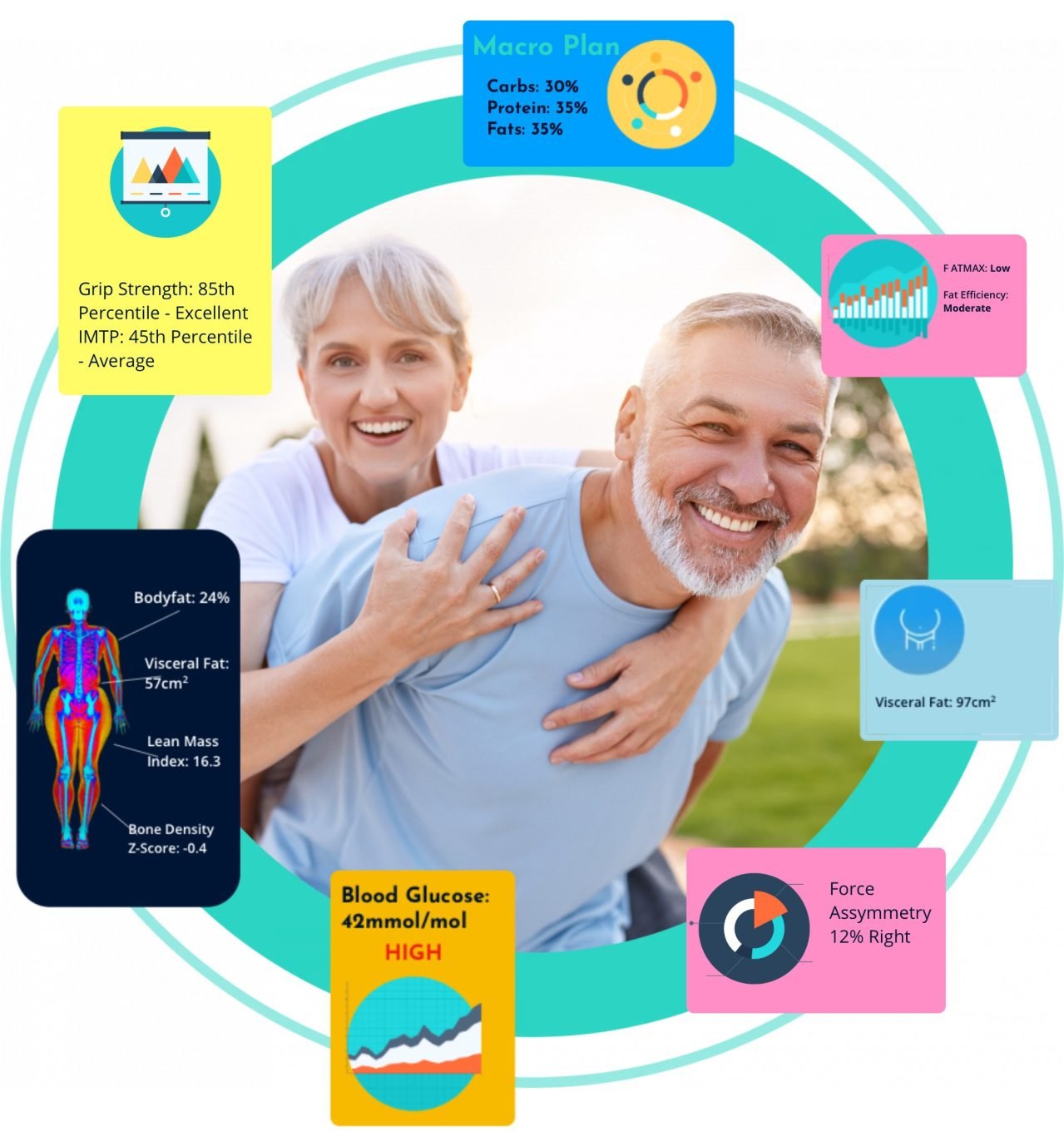
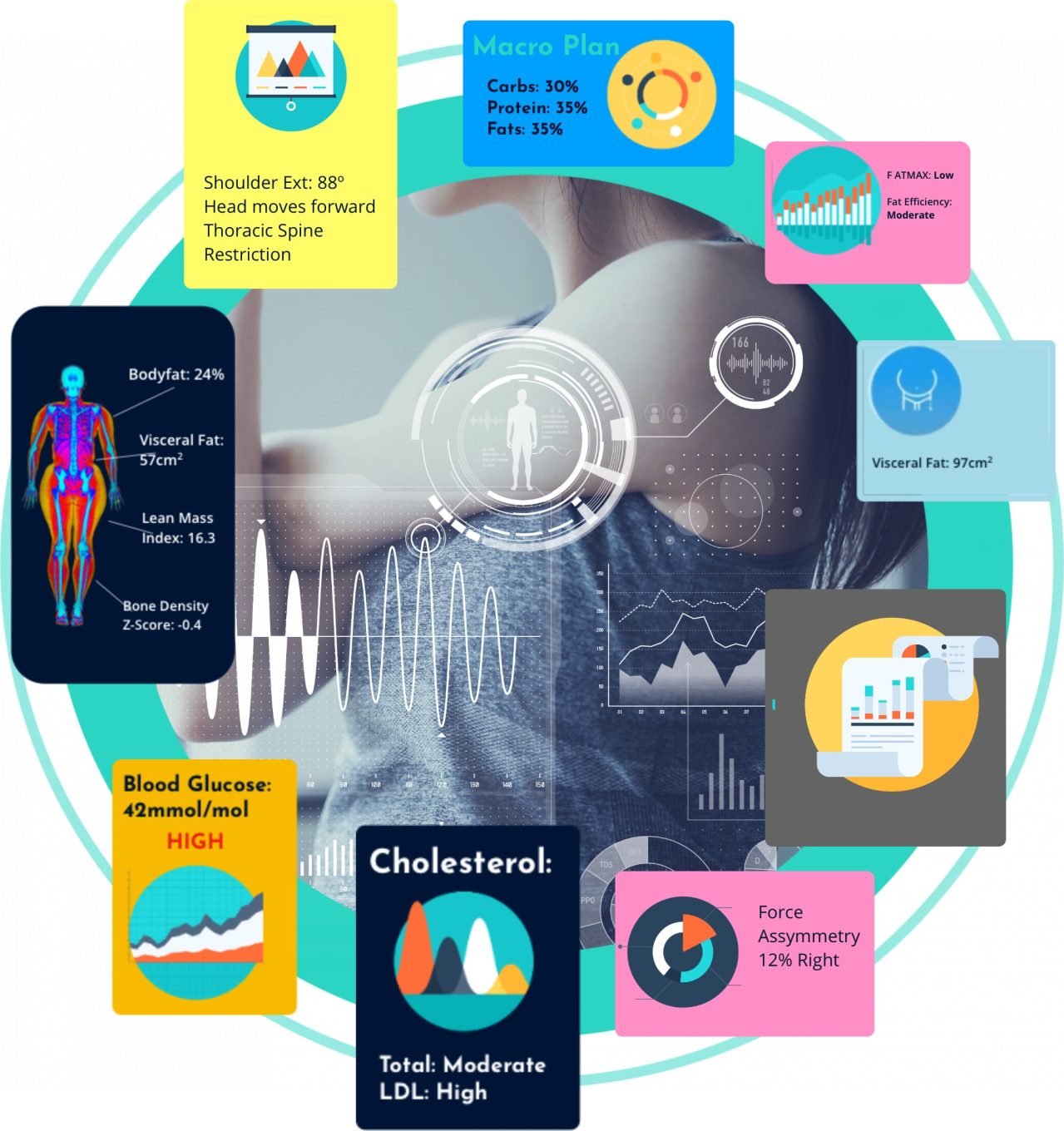
Blood tests for health and fitness are a powerful tool for improving your understanding of your current physical health and highlighting areas for improvement. Not only can blood tests help monitor measures of health such as cholesterol and blood sugar levels, but they can empower you to take steps to reduce your risk of chronic health problems, prioritise longevity, and aid your body composition and fitness goals.
In his best-selling book “Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity”, Dr Peter Attia highlights the importance of taking a proactive approach to health and longevity and recommends 4 blood tests in particular.
In this article, we’ll take a look at these 4 “Outlive” blood tests, as well as other important blood test measures of overall health and fitness.
What are the benefits of blood tests for health and fitness?
Regular blood testing has various benefits – let’s take a look at a few.
Gain baseline measures
One of the main benefits of blood tests is to establish baseline measurements of your overall health. This can help you understand where you’re currently, assess any lifestyle changes you’d like to make, and compare future results to these baseline measures.
It’s important to recognise that “normal” test results exist on a spectrum; for any given blood test, a range of results are categorised as “normal” or “within range”. Even within this “normal” range, there may still be room for improvement to achieve an optimal level for your body specifically. Additionally, for some people, an improvement from an “out of ranger” result to a “normal” result might signal a substantial positive change. For this reason, it’s important to understand where your results typically fall so you can understand your blood test results in relation to your personal medical history.
Reduce the risk of chronic disease
Blood testing is a fantastic way to quickly highlight risk factors for the development of chronic disease, including heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, low bone density, thyroid disorders, and hormonal irregularities.
This is a type of preventative health measure; it helps you to proactively take care of your health before becoming unwell or being diagnosed with a health condition. Some health conditions – such as Type 2 Diabetes – can develop slowly over several years, while initially not causing any noticeable symptoms. Having regular blood tests can help you to identify risk factors (in the case of Type 2 Diabetes, this would be indicated by a high HbA1c result) and take action sooner rather than later.
Make data-informed health decisions
The final benefit of blood testing is that it equips you to make data-informed decisions about your health. With the information provided by testing, you can make informed decisions about lifestyle changes, supplementation, or seeking the advice of a medical professional.
Even if your results come back as within a normal range, having information about your overall health can help empower you to make choices that support your goals: whether that’s prioritising longevity, working towards an athletic personal best, or improving your overall fitness.
Best blood tests for general health
The following blood tests can serve as a starting point for understanding your overall health:
HbA1c test
HbA1c, also known as glycated haemoglobin, is a measure of your blood sugar levels over the last 30 days. You might be familiar with this test as the “blood test for diabetes”, as this test is commonly used as a diagnostic and monitoring test for diabetes and prediabetes. However, the HbA1c test can also be used to determine your risk of developing diabetes, as well as to offer insights into the optimal macronutrient ratio for your body.
The HbA1c blood test works works by looking at the markings which blood sugar leaves on your blood cells. When we have any blood sugar response, a trace of what that response was is left on the blood cell, like a high-water-mark, and this test looks at all these marks. Because our blood cells recycle and renew every 90 days, any HbA1c reading will contain high-water-marks for some blood cells which are just new, and a few which are 80-90 days old. On average this gives us a good picture of what the changes have been in your blood sugar for approximately 30 days.
However, this test can’t tell you the exact levels of glucose, insulin, or other hormones – these can be tested using a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), and C-peptide test. These are more advanced tests, often requested by a medical professional in the management of existing diabetes.
Lipid panel
A lipid panel test refers to a collection of blood tests related to your cholesterol levels, including total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
Getting a blood test for cholesterol done is important as it helps to predict your risk of health events such as heart disease, heart attack, and stroke, as well as serving as an indicator of overall health.
Based on the results of a lipid panel, you might choose to make choices to limit your consumption of saturated fats, include additional sources of unsaturated fat in your diet, increase your activity level, or seek the advice of a GP about other ways to manage high cholesterol.
Thyroid function panel
A thyroid function test is a panel of blood tests that evaluate the function of your thyroid gland, which is responsible for regulating metabolic function.
The panel typically tests the levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3 (free T3 or tri-iodothyronine), and T4 (free T4 or thyroxine) in your blood. A thyroid panel may also include a test for TPOAb (thyroid peroxidase antibodies) or Tg ab (thyroglobulin antibodies) in your blood, particularly if you have a history of an autoimmune thyroid disorder such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Hypothyroidism (an under-active thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (an over-active thyroid) are common thyroid health conditions that can often be treated with medications. Even at subclinical levels, an under-active thyroid can cause symptoms such as weight gain, fatigue, and depression, so it’s worth picking up on early.
Full blood count
A full blood count (FBC) – also known as a complete blood count (CBC) – measures the number of your red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and the haemoglobin present in your blood. This basic test can be used to quickly screen for anaemia, infection, and other medical problems, and is commonly requested by general practitioners, often alongside other blood tests.
Nutritional deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to the development of new health problems, worsen existing health problems, and impact your energy, mood, and sleep.
Some of the most common nutritional deficiencies in the UK include:
- Iron: Essential for the creation of red blood cells; reduces fatigue
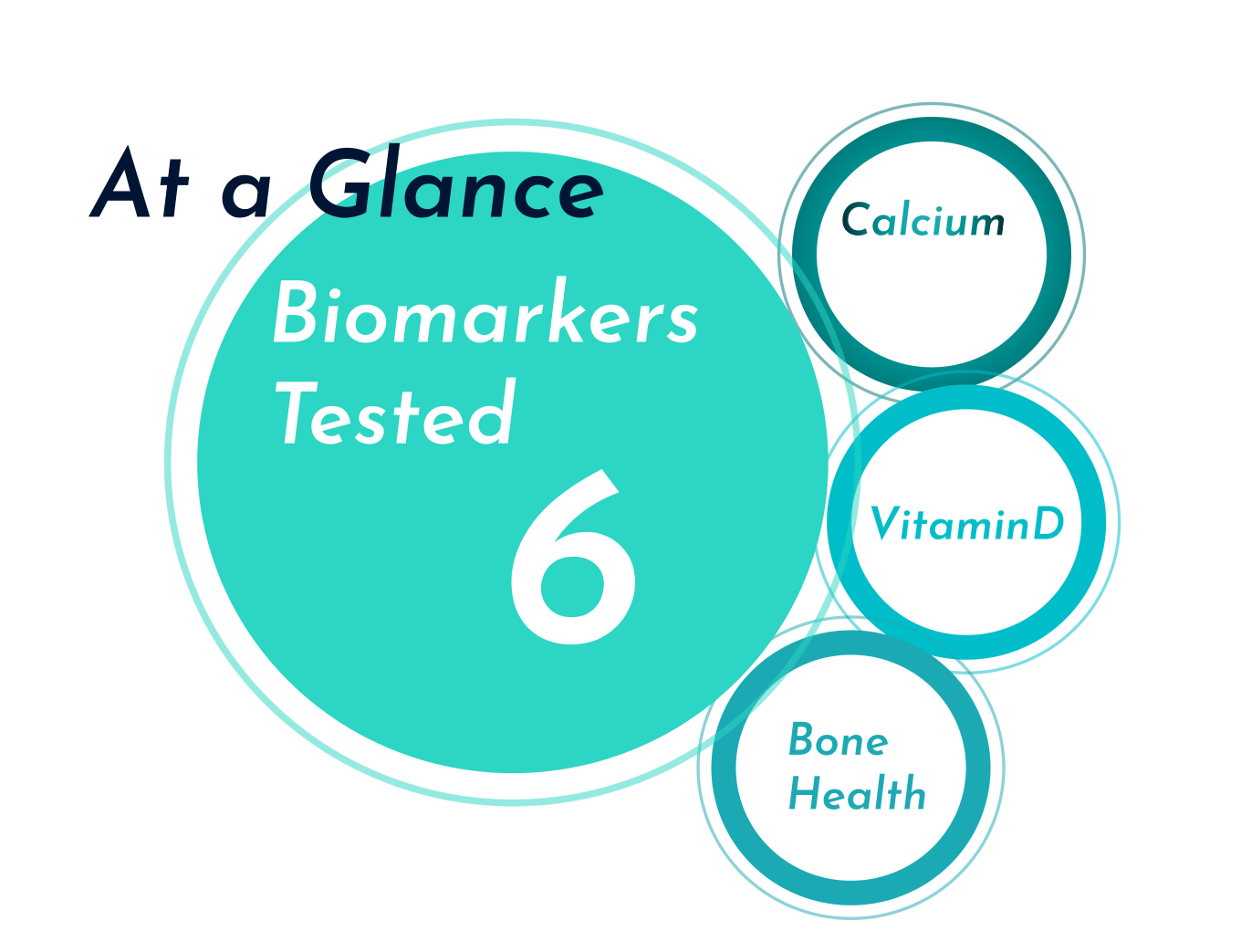
- Calcium: Essential for healthy bones and teeth
- Vitamin D: Essential for healthy bones and muscles and beneficial for a positive mood
- Omega-3: Essential for brain, heart, and eye health, as well as cognition
- Magnesium: Essential for healthy bones, metabolic function, and nerve and muscle function
Blood tests for nutritional deficiencies are a quick and easy way to identify any nutrients you aren’t getting enough of and give you the information you need to make healthy choices regarding nutrition and supplementation (where necessary).
Peter Attia’s recommended blood tests
In addition to the tests outlined above, there are several more specific blood tests that are recommended by Dr Peter Attia in his book, Outlive. These tests might be best suited to someone who already has a baseline understanding of their overall health and fitness, and who is looking for that extra bit of insight into their health.
Lp(a)-P test
The lipoprotein A (Lp(a)-P) test is a blood test that measures the level of lipoprotein A – a type of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) – in your blood.
This test can offer more specificity than a blood test that measures your overall LDL levels. Lipoprotein A is “stickier” than other lipoproteins, and high levels of this specific lipoprotein have been linked to a higher risk of coronary artery disease and cardiac events.
This might be a good test to get if you’re aware of a family history of early-onset heart or blood vessel disease, or to get further insight into high cholesterol levels as shown on a lipid panel test.
LDL-P (or ApoB) test
The LDL-P (low-density lipoprotein particle) test is a blood test that measures the concentration of LDL-P in the blood. This is slightly different to the standard LDL-C test, which measures overall LDL levels in the blood.
Low-density lipoprotein particles are byproducts created in the transport of fats in the body that can contribute to the formation of fatty plaque in the arteries, and lead to the development of coronary artery disease.
The LDL-P test is a good test to have regardless of whether or not you have had high cholesterol results in the past, as LDL-P is a good predictor of cardiovascular disease, and doesn’t always correlate with an overall high LDL cholesterol level.
Similarly, the ApoB (Apolipoprotein B-100) test is a blood test that helps evaluate your overall risk of cardiovascular disease by measuring the amount of Apo B in your blood. Apo B is a protein that works to carry certain types of fat – specifically LDLs – around the body, and is a good predictor of cardiovascular disease. The Apo B test may also be a better predictor of cardiovascular disease in individuals with existing diabetes or a metabolic disorder.
OGTT with insulin measurements
The OGTT (oral glucose tolerance test) is a two-part fasting blood test that measures how well your body can process large quantities of sugar.
This test can be used to screen for Type 2 diabetes as well as to diagnose gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy).
When combined with insulin measurements, the OGTT can be used to determine insulin sensitivity even in individuals without an existing diabetic illness.
ALT
Finally, an ALT test is a blood test used to assess liver function. The ALT test measures the amount of the enzyme alanine transaminase (ALT) in your blood.
High levels of ALT in the blood can be indicative of liver damage, and the test is commonly used to screen for liver disease. This test might be a good idea if you have a family history of liver disease, are diabetic, or have a personal history of heavy alcohol use.
Get on-the-spot blood testing at My Vital Metrics
Curious about how your overall health stacks up? Blood testing at My Vital Metrics offers a quick and easy MOT on key measures of health, including HbA1c blood glucose testing and cholesterol screening.
Whether you’re interested in booking a one-off blood test or receiving a more comprehensive fitness screening, reach out to My Vital Metrics today to find out how we can help you achieve your health and fitness goals.