Cardiovascular fitness/performance, cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF), cardiorespiratory endurance, and aerobic fitness – these terms all refer to a single concept: the body’s capacity to use its cardiac and respiratory systems to effectively deliver oxygen to muscles during sustained exercise.
High cardiovascular fitness is positively associated with lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, increased strength and stamina, and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease.
There are several types of cardiovascular fitness tests available, including the VO2 Max, FatMax test, and 12-minute run test. Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of each test.
VO2 Max
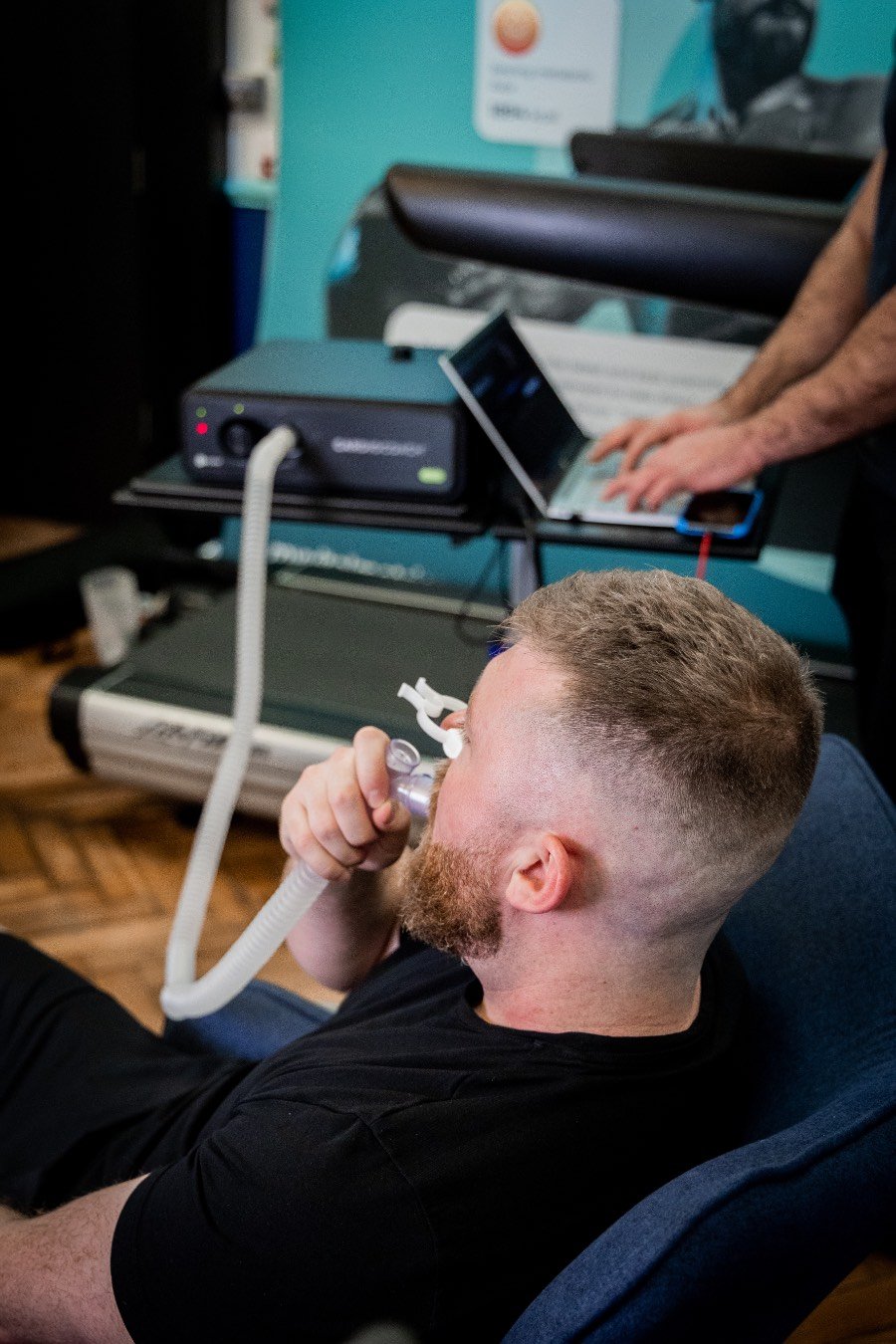
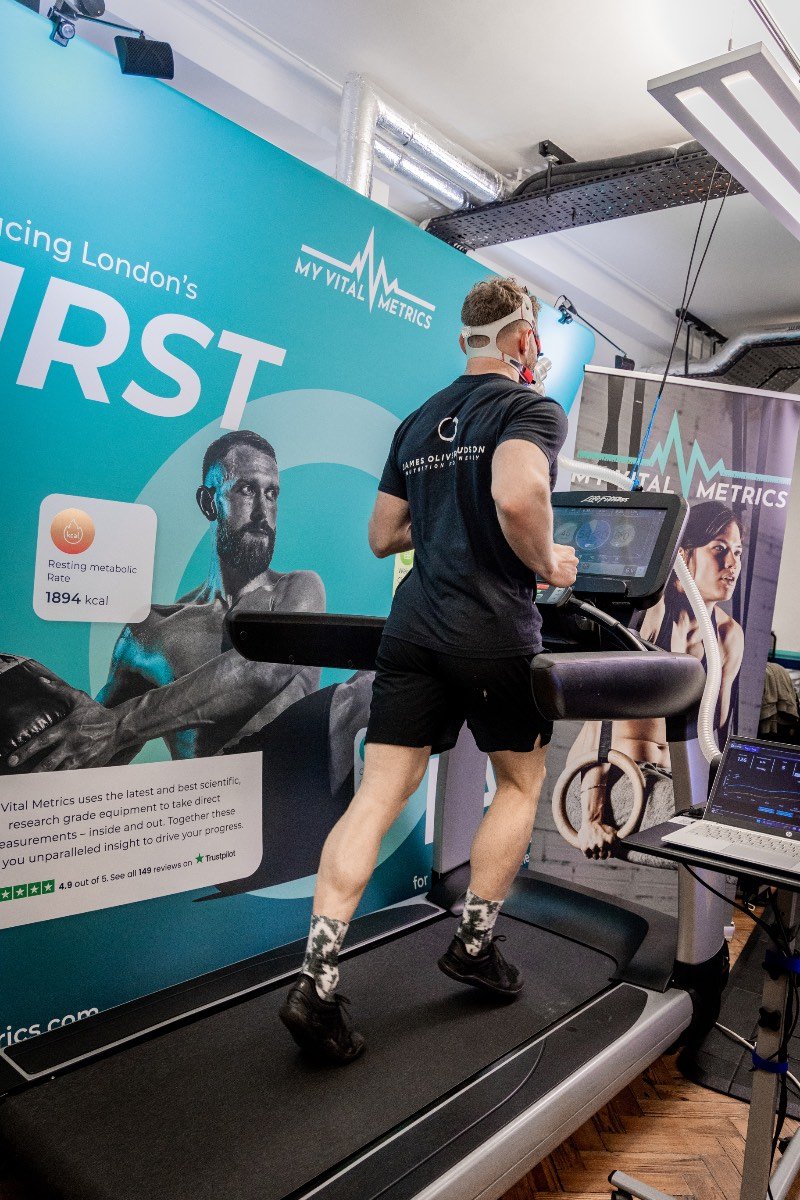
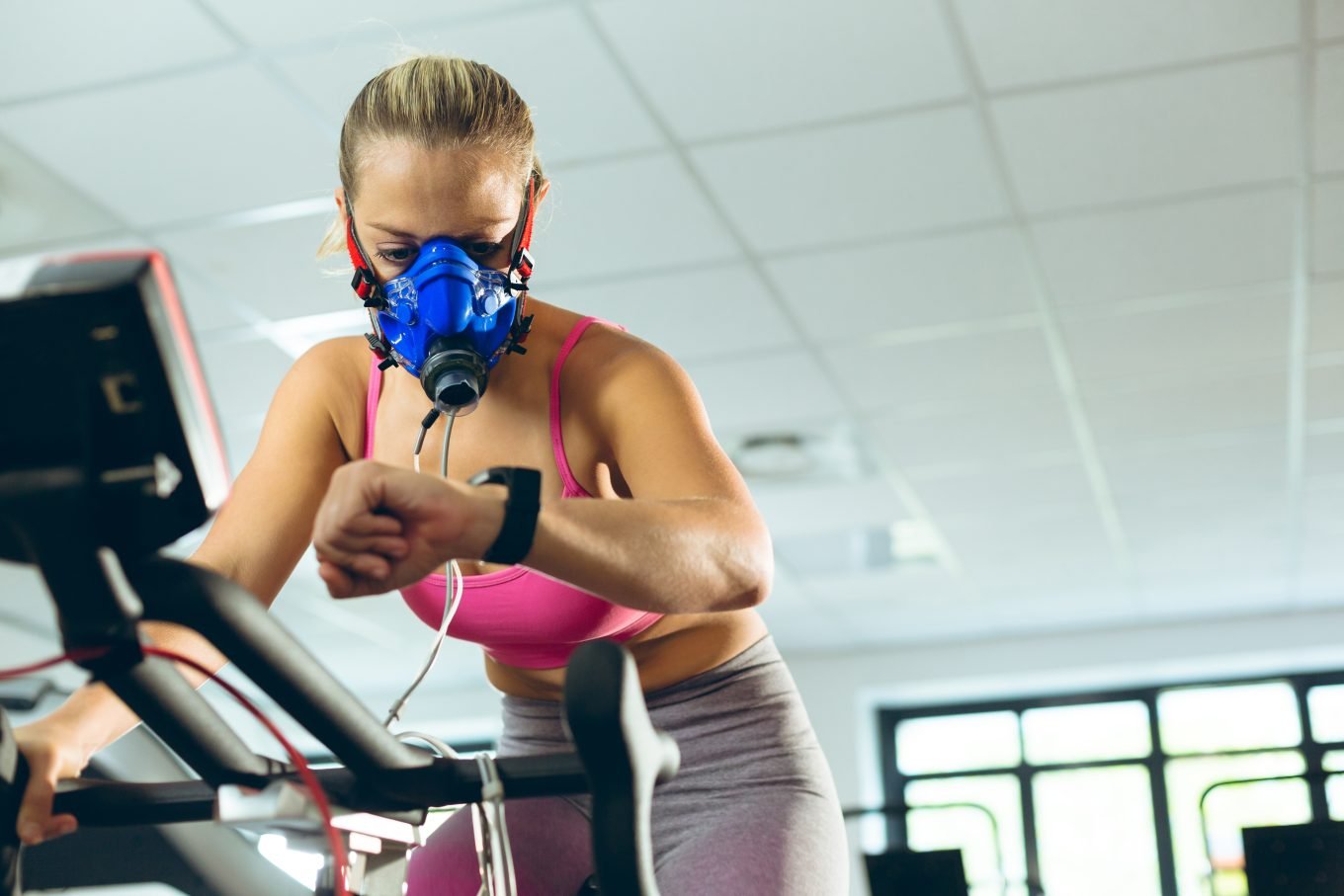
What is it: The gold standard in cardiovascular assessment, the VO2 Max test is a graded exercise test that measures maximal oxygen uptake. The VO2 Max test is measured in mL/kg/min and measures the maximum rate of oxygen that your body can use during intense exercise.
What does it test: Cardiovascular fitness/aerobic endurance
How is it performed: The test-taker performs the test by exercising on a treadmill or stationary bike at a steadily increasing intensity. A face mask is fitted to measure the ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide present in both inhaled and exhaled air throughout the test.
Pros:
- Considered the best indicator of cardiovascular fitness
- Has a high degree of accuracy
- Offers a wealth of data including maximum heart rate, training zones, respiratory rate, aerobic threshold, anaerobic threshold, and information on how the body burns fats and carbohydrates
- Personalised insights for weight loss, fat burning, and training efficiency
Cons:
- Relatively time-consuming
- Can be cost-prohibitive
- Needs to be performed by a trained professional, often in a medical setting or sports performance lab
- The intensive nature of the test means it isn’t suitable for everyone (certain medical conditions may disqualify you from the test without a doctor’s recommendation)
Who is it best for: The VO2 Max test is a great choice for athletes and fitness-oriented individuals looking to maximise their performance at different heart rate intensities and boost their overall capacity to process oxygen.
It’s also a good fit for anybody looking to establish their training zones and how their body utilises fats and carbohydrates during training at varying intervals.
Finally, since VO2 Max is positively correlated with longevity, it’s a great test for anyone seeking to take steps to live a healthier life.
FatMax test
What is it: The FatMax test is a measure of fat oxidation that identifies the intensity of exercise at which the test-taker’s fat-burning potential is greatest. The test shows the ranges of heart rates at which the test-taker is currently best at burning fat due to exercise and can reveal the ideal training intensity for them to be working at to make use of the good work done and expand upon it.
What does it test: The FatMax test measures oxygen and carbon dioxide output during exercise. The ratio of these gases provides information about the fuel source being used at a particular intensity of exercise. At a given time, a 1:1 ratio of carbon dioxide to oxygen indicates that the test-taker is using carbohydrates as fuel, while a 0.7:1 ratio indicates the test-taker is using fat as fuel.
How is it performed: The FatMax test is typically performed on a treadmill. The test-taker is fitted with a heart rate strap and a mask which monitors the ratio of oxygen to carbon dioxide inhaled and exhaled throughout the test. Starting at a low intensity, the test-taker walks on the treadmill at increasing inclines until fat oxidation reaches a peak level and starts to decline, at which point the test concludes.
Pros:
- Offers insights about how to train most efficiently for fat-burning
- Helps you to get the most out of your cardio workouts
- Identify the optimal fat-burning heart rate for your body
- Not a high-intensity test and is accessible to most people
Cons:
- Needs to be performed with specialist equipment
- Requires expert interpretation to make the most of the data
Who is it best for: The FatMax test is great for anyone looking to understand how their body burns fuel, or looking to burn fat in the most efficient way possible. Since it doesn’t require reaching as high an intensity of exercise as the VO2 Max test, it’s an accessible option regardless of fitness level.
12-minute run test
What is it: The 12-minute run test, or Cooper test, is a fitness test designed to determine aerobic fitness by offering an estimate of VO2 Max. Originally developed by Kenneth Cooper to estimate the fitness levels of military personnel, the 12-minute run test requires the test-taker to walk or run as far as they can within a 12-minute interval.
What does it test: Aerobic endurance. The result of the test (in either miles or kilometres), is inserted into a formula to produce an estimate of VO2 Max, given in ml/kg/min. Online fitness calculators allow test-takers to easily compare their scores with those in their age and gender bracket.
Pros:
- The 12-min run test is simple, and be carried out anywhere, by anyone
- The test is accessible: for those who aren’t able to run, the test can be carried out at a walking pace
Cons:
- The test offers an estimate of VO2 Max, not an exact calculation
- Variables such as location, surface, humidity, temperature, and motivation can prevent replicable results
Who is it best for: The 12-minute run test is best for those looking to quickly estimate their aerobic endurance for free, and who are confident in their ability to run or walk for 12 minutes safely.
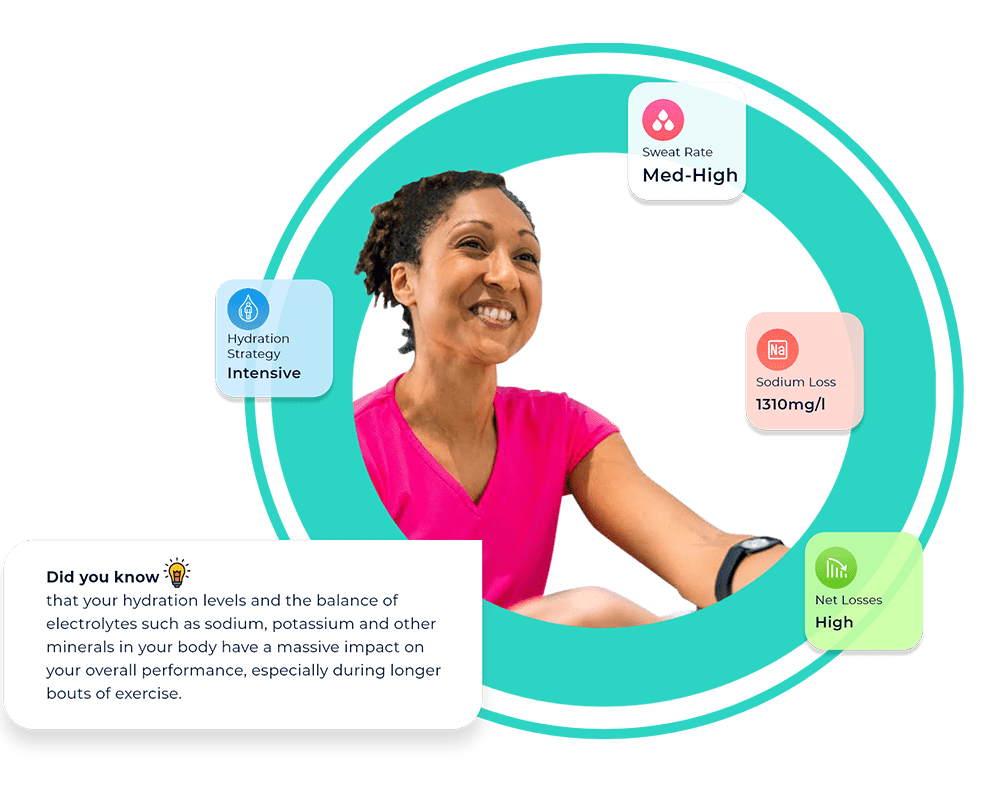
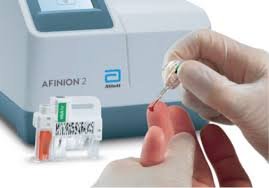
Blood tests for health and fitness
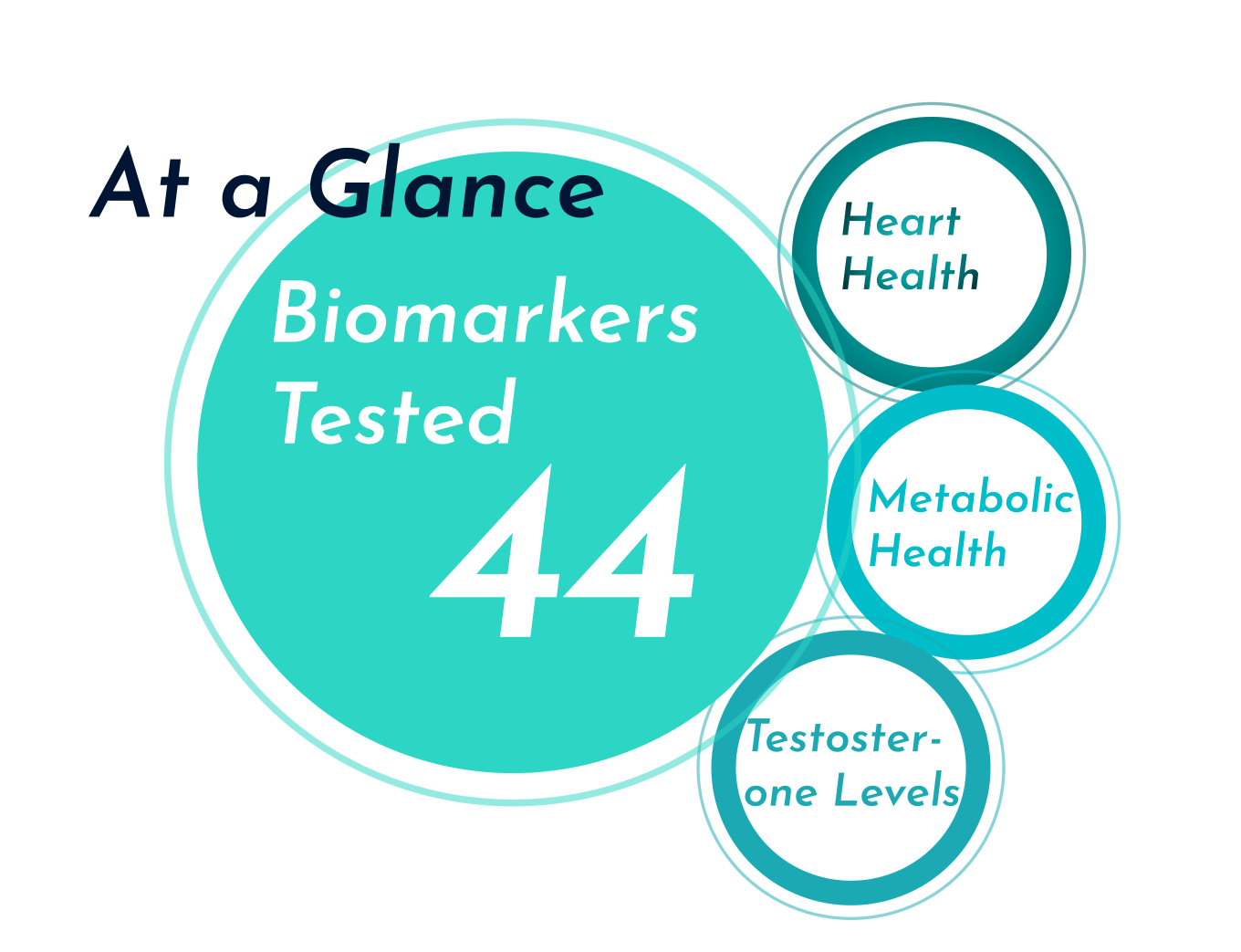
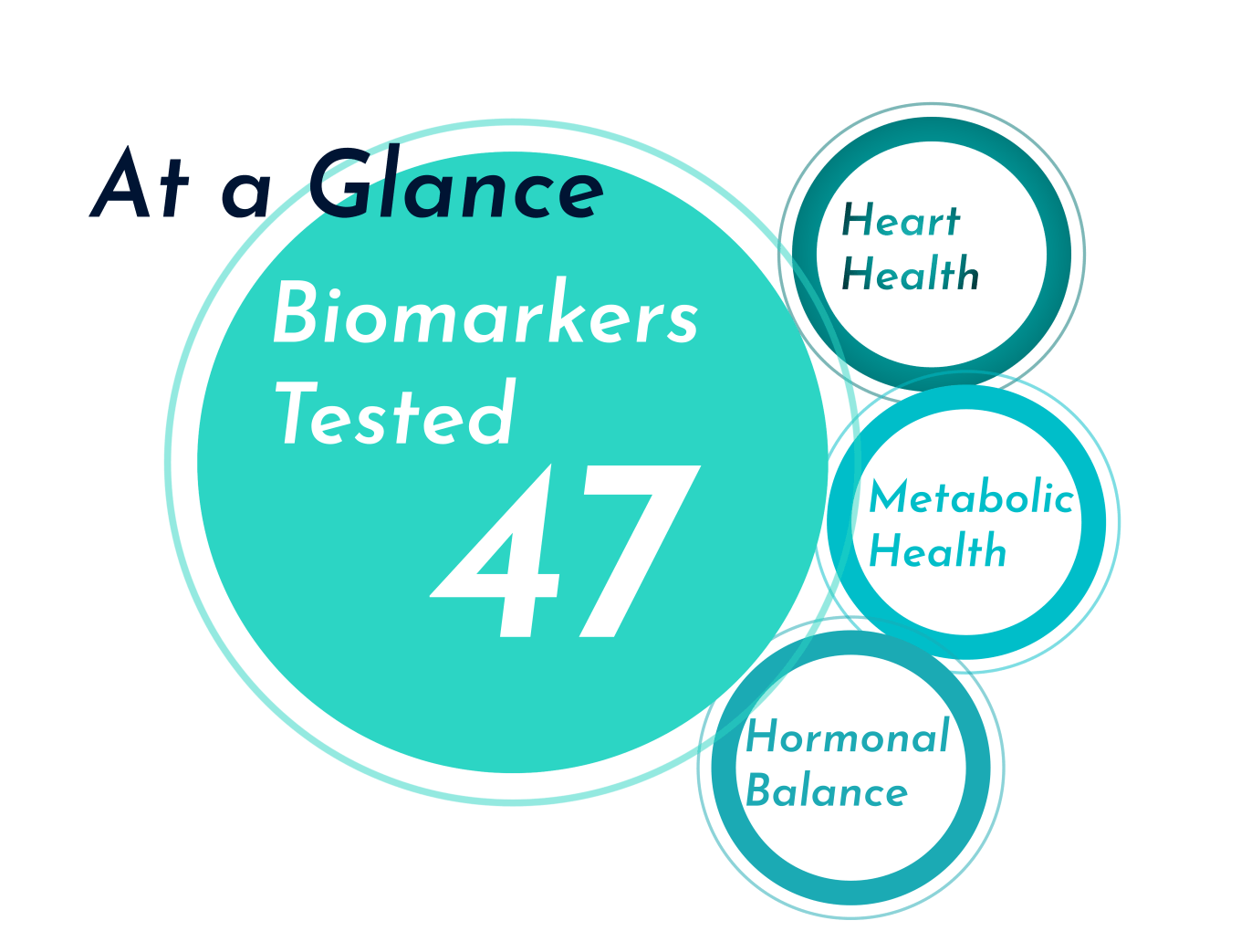
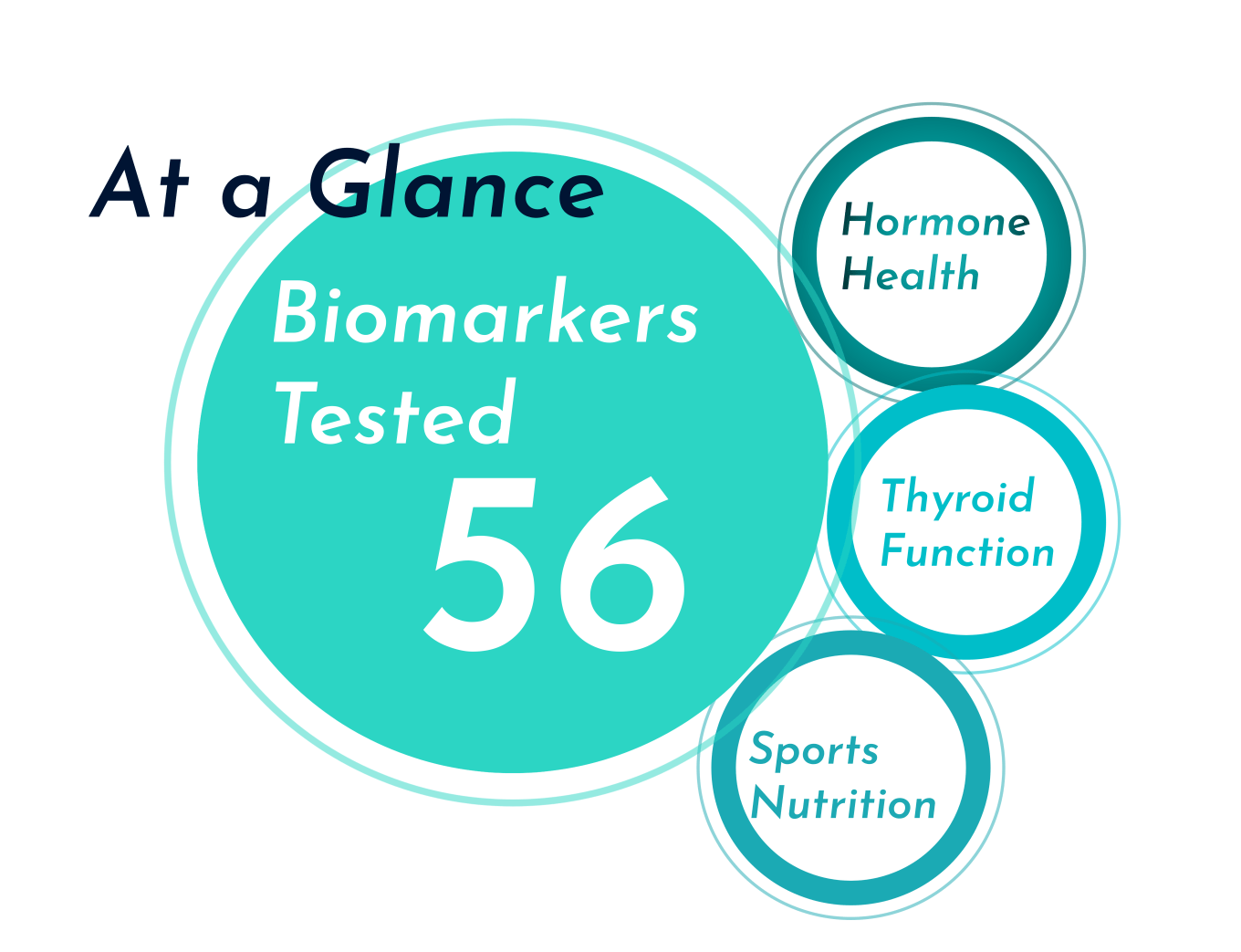
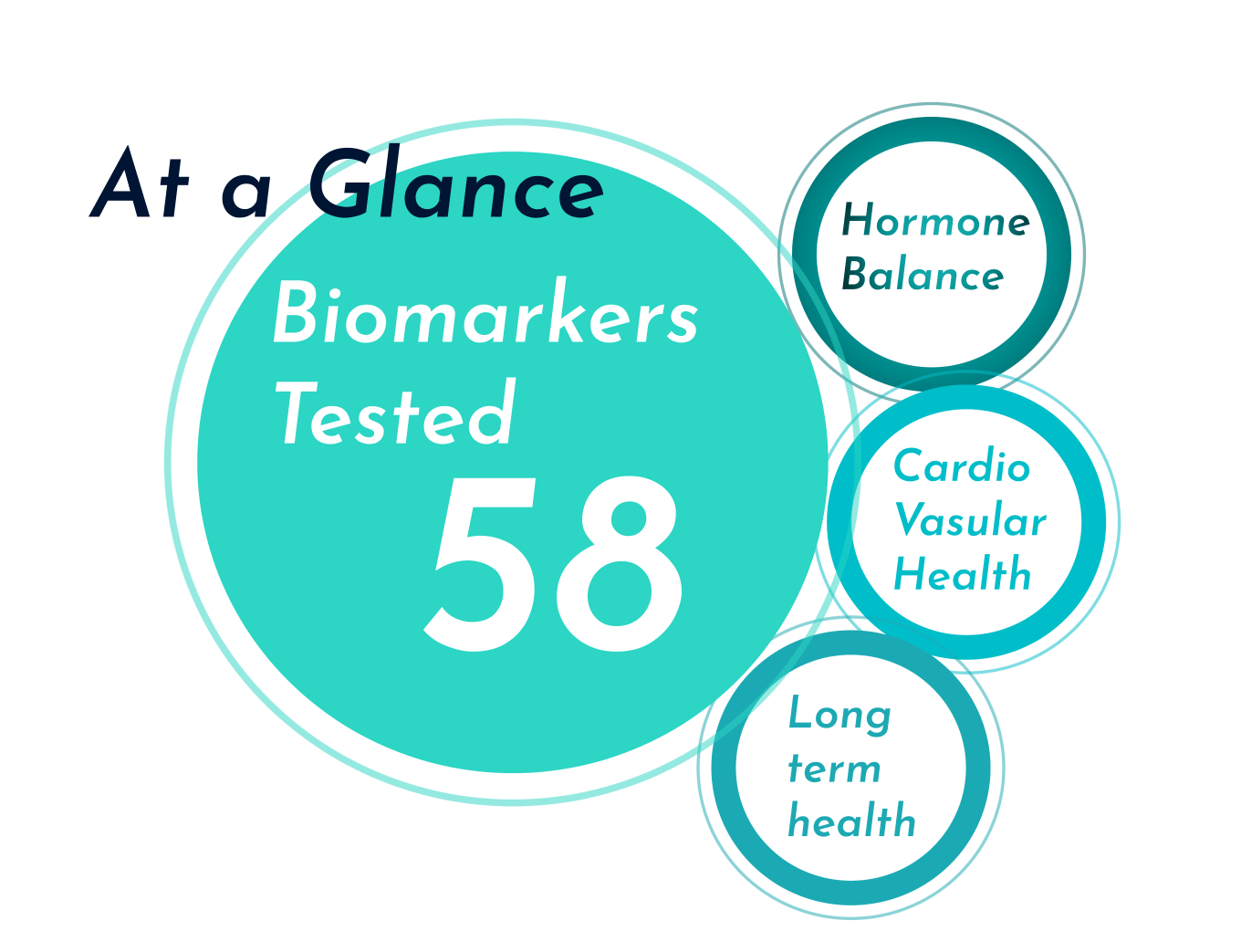
What is it: Blood tests are a simple way to test common health indicators such as cholesterol levels, thyroid function, blood sugar levels, hormone levels, and more. These tests might be requested by your GP or medical specialist or can be proactively booked through a pharmacy, online health clinic, or health and fitness lab.
What does it test: Some popular blood tests for health and fitness include:
- HbA1c: A diagnostic test for diabetes and pre-diabetes, the HbA1c blood test is a blood sugar test that measures the amount of blood glucose attached to haemoglobin in your blood.
- Lipid panel: A cholesterol test that calculates total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides.
- FBC: A full blood count (FBC) measures the quantity of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and haemoglobin present in your blood. This test can be used to screen for anaemia, infection, and other medical problems.
- Thyroid function test: Tests T3, T4, and TSH levels to assess how well the thyroid gland is working and to diagnose thyroid disorders.
- Hormone tests: Tests for oestrogen, testosterone, and cortisol levels can be used to identify hormonal imbalances.
How is it performed: A blood test can be performed in two ways:
- Venous blood test: Blood is collected from a vein (typically in the arm) using a needle
- Fingerprick blood test: Blood is collected from the fingertip using a lancet.
A venous blood test is the standard in medical settings, while a fingerprick blood test can be carried out at home or in another testing setting. The main advantages of a fingerprick blood test are that they are quick and easy to carry out, and tend to be experienced as less invasive.
Pros:
- Quickly highlight key markers of overall health
- Flag areas of concern that are worth raising with your GP
- Suggest types of lifestyle changes that might benefit your health
- Often free or cheap to have performed
Cons:
- Only test certain health markers
- Don’t offer a complete picture of overall health and fitness
Who is it best for: A blood test for health and fitness (or combination of blood tests) is a great starting place for anybody looking to prioritise their overall health or check on their blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Muscular endurance tests